Lecture #1: Course Intro & Relational Model
Course Outline
- Relational Databases
- Storage
- Execution
- Concurrency Control
- Recovery
- Distributed Databases
- Potpourri
Databases
DATABASE
Organized collection of inter-related data that models some aspect of the real-world.
Databases are core the component of most computer applications.
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
A DBMS is software that allows applications to store and analyze information in a database.
A general-purpose DBMS is designed to allow the definition, creation, querying, update, and administration of databases.
DATA MODELS
A data model is collection of concepts for describing the data in a database.
A schema is a description of a particular collection of data, using a given data model.
DATA MODEL
- Relational
- Key/Value
- Graph
- Document
- Column-family
- Array / Matrix
- Hierarchical
- Network
- Multi-Value
RELATIONAL MODEL
Structure: The definition of the database’s relations and their contents. 数据库关系及其内容的定义。
Integrity: Ensure the database’s contents satisfy constraints.
Manipulation: Programming interface on how to access and modify a database’s contents.
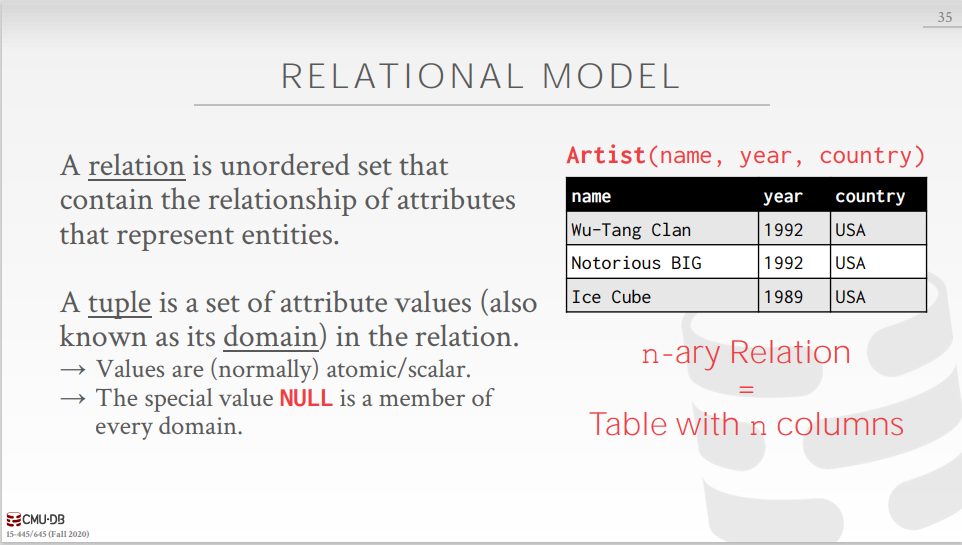

A relation is unordered set that contain the relationship of attributes that represent entities.
A tuple is a set of attribute values (also known as its domain) in the relation.
→ Values are (normally) atomic/scalar.
→ The special value NULL is a member of every domain.
RELATIONAL MODEL: PRIMARY KEYS
A relation’s primary key uniquely identifies a single tuple.
Some DBMSs automatically create an internal primary key if a table does not define one.
Auto-generation of unique integer primary keys:
→ SEQUENCE (SQL:2003)
→ AUTO_INCREMENT (MySQL)
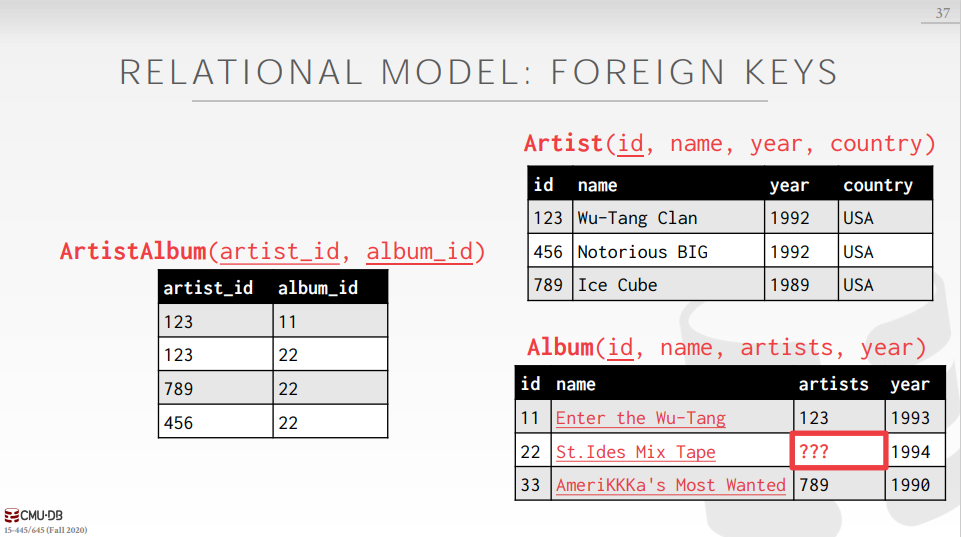
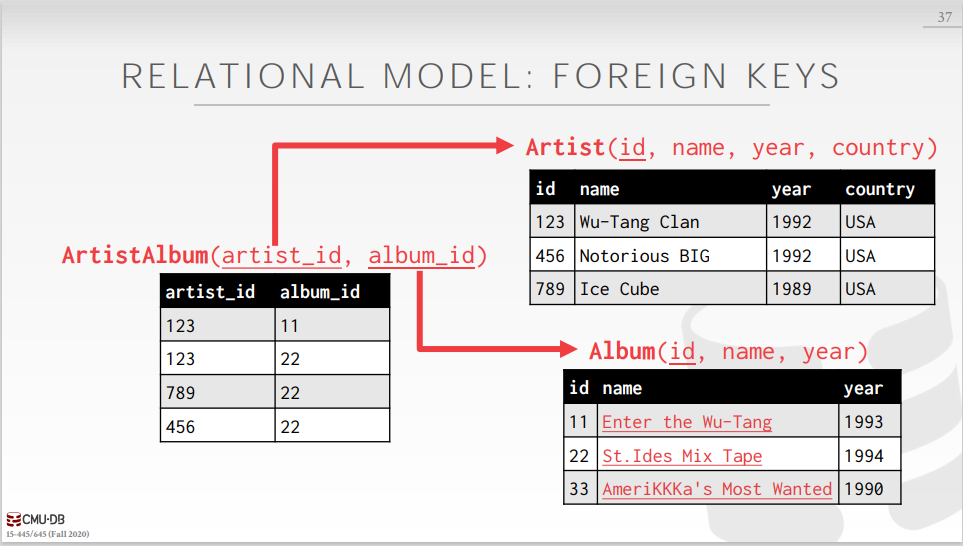
RELATIONAL MODEL: FOREIGN KEYS
A foreign key specifies that an attribute from one relation has to map to a tuple in another relation.


DATA MANIPULATION LANGUAGES (DML)
Methods to store and retrieve information from a database.
Procedural:
→ The query specifies the (high-level) strategy the DBMS should use to find the desired result.
Non-Procedural:
→ The query specifies only what data is wanted and not how to find it.
.png)
RELATIONAL ALGEBRA
Fundamental operations to retrieve and manipulate tuples in a relation. → Based on set algebra.
Each operator takes one or more relations as its inputs and outputs a new relation.
→ We can “chain” operators together to create more complex operations.


SELECT
Choose a subset of the tuples from a relation that satisfies a selection predicate.
PROJECTION
Generate a relation with tuples that contains only the specified attributes.
UNION
Generate a relation that contains all tuples that appear in either only one or both input relations.
INTERSECTION
Generate a relation that contains only the tuples that appear in both of the input relations.
DIFFERENCE
Generate a relation that contains only the tuples that appear in the first and not the second of the input relations.
PRODUCT
Generate a relation that contains all possible combinations of tuples from the input relations.
JOIN
Generate a relation that contains all tuples that are a combination of two tuples (one from each input relation) with a common value(s) for one or more

attributes.
OBSERVATION
Relational algebra still defines the high-level steps of how to compute a query.
A better approach is to state the high-level answer that you want the DBMS to compute.
→ Retrieve the joined tuples from R and S where b_id equals 102.
因为relational algebra还是对于人类来说太抽象,所以有了query语言
RELATIONAL MODEL: QUERIES
The relational model is independent of any query language implementation.
SQL is the de facto standard (many dialects).
CONCLUSION
Databases are ubiquitous.
Relational algebra defines the primitives for processing queries on a relational database.
We will see relational algebra again when we talk about query optimization + execution.